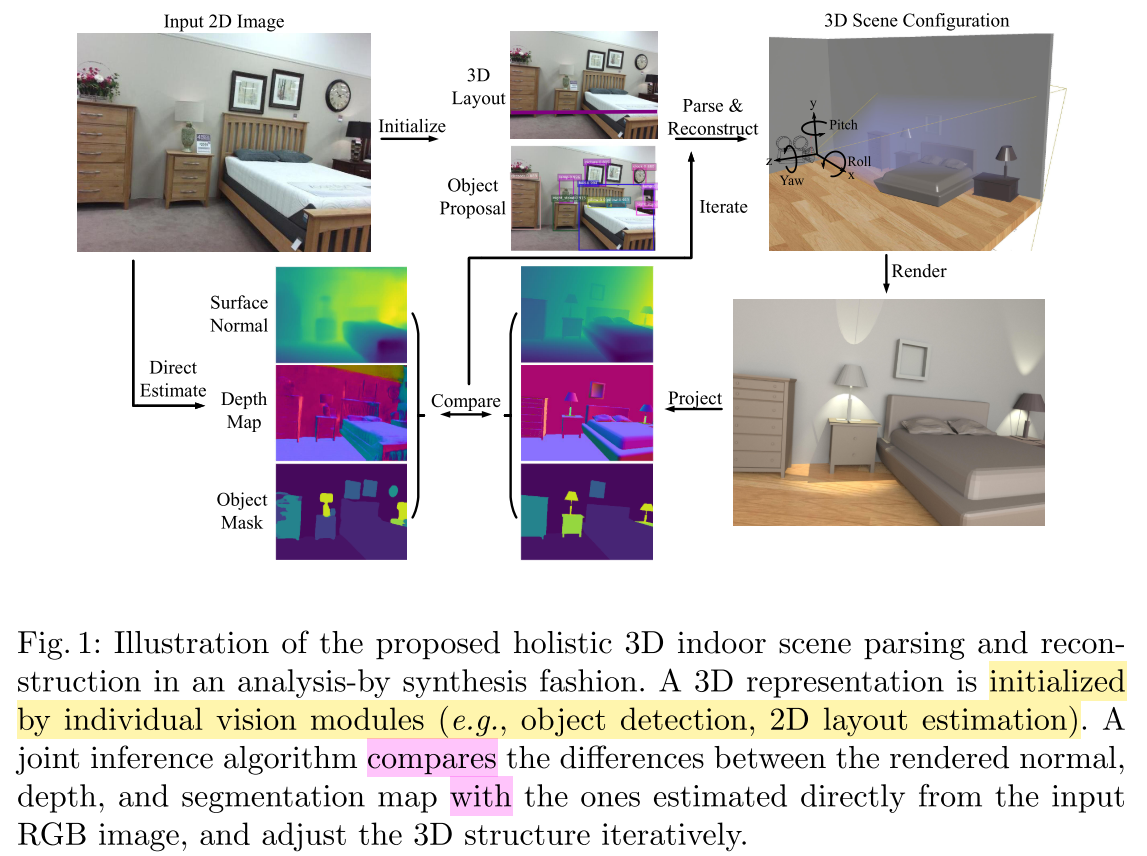
这篇文章和上一篇出自同一个作者,都是做3D场景理解和重建的,研究的内容有很多重叠,研究的方法有所区别,可以看到对一个问题做深入之后,能同时出几篇文章。这篇文章使用深度学习和概率模型相结合的方法,并且多了场景重建的部分,其中一些细节描述更细。
-
论文名称:Holistic 3D Scene Parsing and Reconstruction from a Single RGB Image
-
论文作者:Siyuan Huang, Siyuan Qi, Yixin Zhu, Yinxue Xiao, Yuanlu Xu, Song-Chun Zhu(来自UCLA)
-
收录情况:ECCV 2018
简介
本文提出一种方法——Holistic Scene Grammar(HSG),利用单张RGB图片解析和重建3D场景,重建的时候用到了一些CAD模型。HSG 能表示3D场景的结构信息,刻画室内场景的功能 + 几何空间的联合分布特性(functional and geometric space)。HSG 捕捉到了室内场景隐含的几方面维度:
- latent human context, describing the affordance and the functionality of a room arrangement
- geometric constraints over the scene configuration
- physical constraints that guarantee physically plausible parsing and reconstruction
本文采用 analysis-by-synthesis 方式进行 parsing & reconstruction,使得输入图像和渲染后的图像的差异在以下几个方面最小化:
- space of depth
- surface normal(表面法向量)
- object segmentation map
优化时,模型被表示成一个语法解析图——parse graph,使用 Markov Chain Monte Carlo 进行推理,这样就能够对不可导的解空间进行优化,比如
- object localization
- 3D layout
- hidden human context
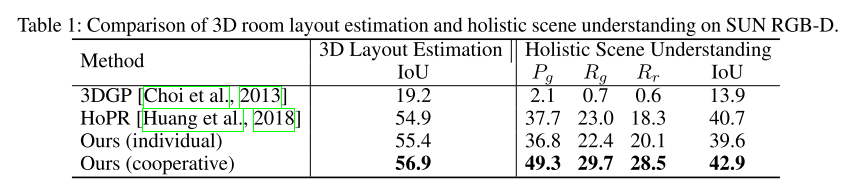
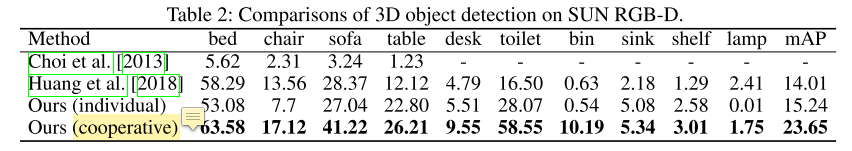
在SUN RGB-D的实验达到了3D layout estimation, 3D object detection, scene understanding当前最优。
相关工作
- scene parsing
- discriminative approaches
- Dai, J., He, K., Sun, J.: Boxsup: Exploiting bounding boxes to supervise convolu- tional networks for semantic segmentation. In: ICCV. (2015)
- Noh, H., Hong, S., Han, B.: Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmen- tation. In: ICCV. (2015)
- Zheng, S., Jayasumana, S., Romera-Paredes, B., Vineet, V., Su, Z., Du, D., Huang, C., Torr, P.H.: Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. In: ICCV. (2015)
- Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) (2017)
- Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. (2015)
- Lin, G., Milan, A., Shen, C., Reid, I.: Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. (2017)
- Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR. (2017)
- generative approaches
- Zhao, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Image parsing with stochastic scene grammar. In: Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). (2011)
- Zhao, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Scene parsing by integrating function, geometry and appear- ance models. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Choi, W., Chao, Y.W., Pantofaru, C., Savarese, S.: Understanding indoor scenes using 3d geometric phrases. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Lin, D., Fidler, S., Urtasun, R.: Holistic scene understanding for 3d object detection with rgbd cameras. In: ICCV. (2013)
- Guo, R., Hoiem, D.: Support surface prediction in indoor scenes. In: ICCV. (2013)
- Zhang, Y., Song, S., Tan, P., Xiao, J.: Panocontext: A whole-room 3d context model for panoramic scene understanding. In: ECCV. (2014)
- Zhang, Y., Song, S., Yumer, E., Savva, M., Lee, J.Y., Jin, H., Funkhouser, T.: Physically-based rendering for indoor scene understanding using convolutional neu- ral networks. In: CVPR. (2017)
- Zou, C., Li, Z., Hoiem, D.: Complete 3d scene parsing from single rgbd image. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09490 (2017)
- discriminative approaches
- scene reconstruction from a single image
-
- Hedau, V., Hoiem, D., Forsyth, D.: Recovering the spatial layout of cluttered rooms. In: CVPR. (2009)
- Lee, D.C., Hebert, M., Kanade, T.: Geometric reasoning for single image structure recovery. In: CVPR. (2009)
- Mallya, A., Lazebnik, S.: Learning informative edge maps for indoor scene layout prediction. In: ICCV. (2015)
- Dasgupta, S., Fang, K., Chen, K., Savarese, S.: Delay: Robust spatial layout esti- mation for cluttered indoor scenes. In: CVPR. (2016)
- Ren, Y., Li, S., Chen, C., Kuo, C.C.J.: A coarse-to-fine indoor layout estimation (cfile) method. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV). (2016)
- Izadinia, H., Shan, Q., Seitz, S.M.: Im2cad. In: CVPR. (2017)
- Lee, C.Y., Badrinarayanan, V., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: Roomnet: End- to-end room layout estimation. In: ICCV. (2017)
- Zhao, H., Lu, M., Yao, A., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, L.: Physics inspired op- timization on semantic transfer features: An alternative method for room layout estimation. In: CVPR. (2017)
-
- Salas-Moreno, R.F., Newcombe, R.A., Strasdat, H., Kelly, P.H., Davison, A.J.: Slam++: Simultaneous localisation and mapping at the level of objects. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Aubry, M., Maturana, D., Efros, A.A., Russell, B.C., Sivic, J.: Seeing 3d chairs: exemplar part-based 2d-3d alignment using a large dataset of cad models. In: CVPR. (2014)
- Lim, J.J., Khosla, A., Torralba, A.: Fpm: Fine pose parts-based model with 3d cad models. In: ECCV. (2014)
- Song, S., Xiao, J.: Sliding shapes for 3d object detection in depth images. In: ECCV. (2014)
- Tulsiani, S., Malik, J.: Viewpoints and keypoints. In: CVPR. (2015)
- Bansal, A., Russell, B., Gupta, A.: Marr revisited: 2d-3d alignment via surface normal prediction. In: CVPR. (2016)
- Song, S., Xiao, J.: Deep sliding shapes for amodal 3d object detection in rgb-d images. In: CVPR. (2016)
- Wu, J., Xue, T., Lim, J.J., Tian, Y., Tenenbaum, J.B., Torralba, A., Freeman, W.T.: Single image 3d interpreter network. In: ECCV. (2016)
- Deng, Z., Latecki, L.J.: Amodal detection of 3d objects: Inferring 3d bounding boxes from 2d ones in rgb-depth images. In: CVPR. (2017)
-
- Zhao, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Scene parsing by integrating function, geometry and appear- ance models. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Choi, W., Chao, Y.W., Pantofaru, C., Savarese, S.: Understanding indoor scenes using 3d geometric phrases. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Song, S., Lichtenberg, S.P., Xiao, J.: Sun RGB-D: A RGB-D scene understanding benchmark suite. In: CVPR. (2015)
- Song, S., Yu, F., Zeng, A., Chang, A.X., Savva, M., Funkhouser, T.: Semantic scene completion from a single depth image. In: CVPR. (2017)
-
- scene grammer
- Jiang, Y., Koppula, H., Saxena, A.: Hallucinated humans as the hidden context for labeling 3d scenes. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Zhao, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Image parsing with stochastic scene grammar. In: Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). (2011)
- Zhao, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Scene parsing by integrating function, geometry and appear- ance models. In: CVPR. (2013)
- Jiang, Y., Saxena, A.: Modeling high-dimensional humans for activity anticipation using gaussian process latent crfs. In: Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS). (2014)
Holistic Scene Grammar
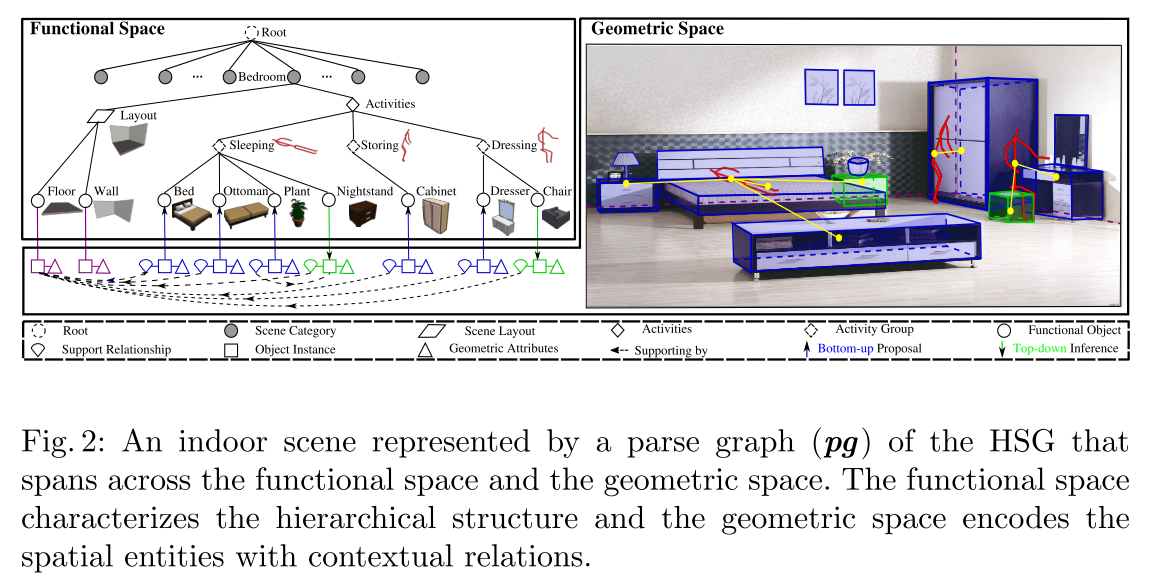
- HSG的组成
- 功能空间$\mathbb{F}$中 latent hierarchy structure
- 几何空间$\mathbb{G}$中的 terminal object entities
-
对于人工合成的环境,几何空间中物体的排列布置,应该来自功能空间的投影(???如何理解这句话)
-
功能空间被建模成概率上下文无关文法 $probabilistic ~context~free~grammar$(PCFG),用来捕获功能群组(functional groups)的等级结构;几何空间捕获物体的空间上下文(spatial context among objects)关系,捕获的方式是在terminal nodes上定义一个 Markov Random Field;这两个空间共同构成了随机上下文敏感文法 $stochastic~context-sensitive~grammar$(SCSG)—— 就是指本文的HSG
-
HSG 从场景根节点出发,到终端节点结束。一个室内场景能表示成一张 parse graph($\textbf{pg}$),如上图所示。
- 形式化定义:HSG表示为一个5元组$\langle S, V, R, E, P \rangle$
- S 是室内场景的根节点
- V 是顶点集,包括非终端节点$V_f \in \mathbb{F}$和终端节点$V_g \in \mathbb{G} $
- R 是生产规则
- E 是终端节点间的上下文关系,对应$\textbf{pg}$中的水平links(图中紫色、蓝色、绿色块间的水平连接)
- P 是定义在$\textbf{pg}$的概率模型
- 功能空间$\mathbb{F}$:非终端节点 \(V_f = {V_f^c, V_f^a, V_f^o, V_f^l} \in \mathbb{F}\)
- 场景类别节点$V_f^c$
- 场景类别节点$V_f^a$
- 场景类别节点$V_f^o$
- 场景类别节点$V_f^l$
- 几何空间$\mathbb{G}$:终端节点 \(V_g = {V_g^o, V_g^l} \in \mathbb{G}\),是 ojbect entities 和 room layout的CAD models
- 物体表示为一个CAD模型
- 物体外观参数:3D size,location, orientation
- 房间布局表示为一个立方体,进一步分解成房间的5个平面——left、right、middle wall、floor、ceiling(???为什么立方体会分出来5个平面)
- 生产规则$R$
- $S \rightarrow V^c_f$: scene → category 1 | category 2 | . . . (e.g., scene → office | kitchen)
- $V_f^c \rightarrow V^a_f$: category → activity groups · layout (e.g., office → (walking,reading) · layout)
- $V_f^c \rightarrow V^a_f$: activity group → functional objects (e.g., sitting → (desk, chair))
- 其中,$\cdot$ 表示 determinstic decomposition;$|$ 表示alternative explanations;() 表示组合
- 形式化定义:HSG表示为一个5元组$\langle S, V, R, E, P \rangle$
- 最后,a scene configuration 能表示成一个$\textbf{pg}$,终端节点是物体和布局,\(\textbf{pg} = \{pg_f, pg_g\}, E \in pg_g\)
Inference
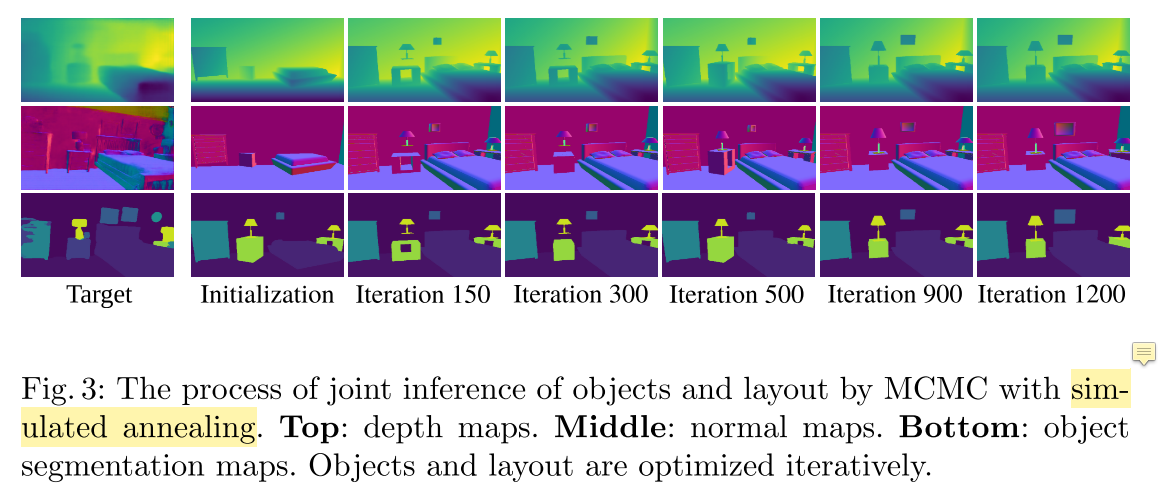

实验
- 数据集:SUN RGB-D(在好多类似论文用了)
-
评测任务:3D scene parsing, 3D reconstruction, 3D scene understanding
-
Qualitative Results
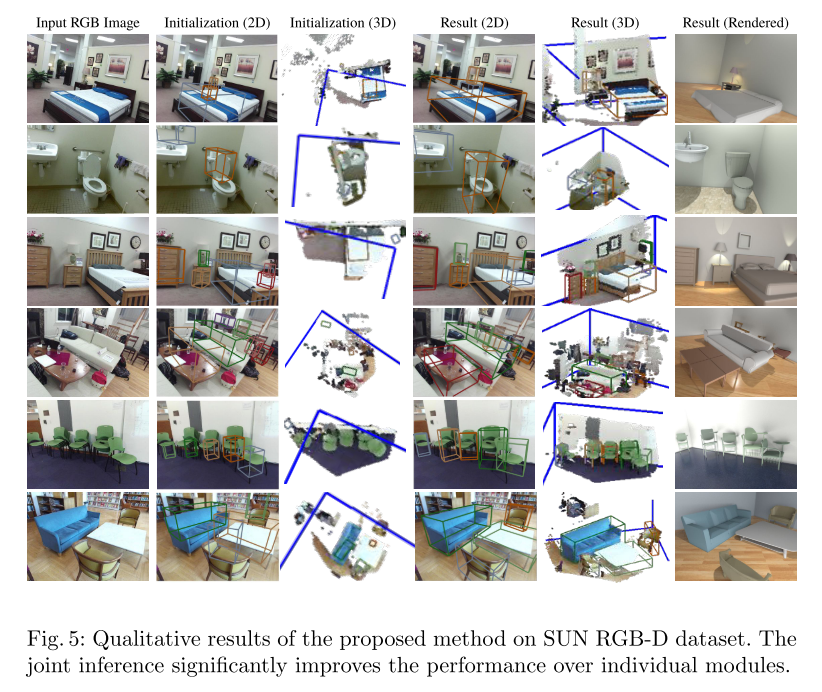

- Quatitative Results